Image source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25400448
Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme found in all tissues in the human body. In balance, it protects your gut against harmful bacteria and aids digestion. However, high blood levels usually point to liver or bone problems. Read on to understand the symptoms and causes of high alkaline phosphatase and how to reduce it naturally.
What Does High Alkaline Phosphatase Mean?
The normal range of alkaline phosphatase in the blood is 20 to 140U/L, although this can vary from lab to lab. Children and pregnant women can have significantly higher levels of the enzyme in their blood [1].
Values above 130 U/L are usually considered to be high.
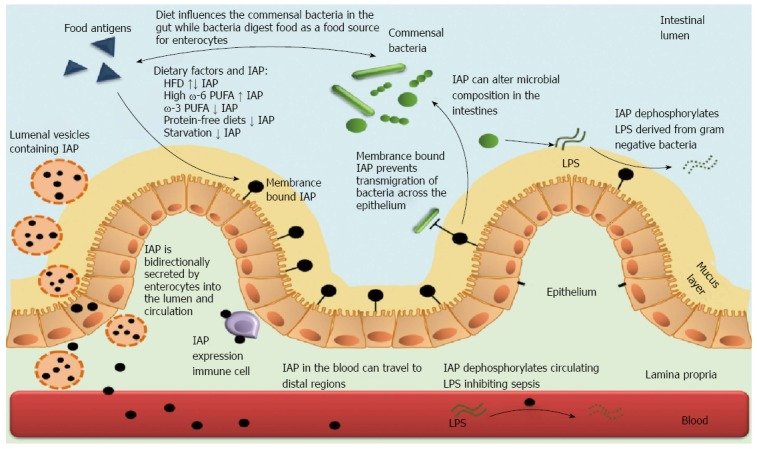
Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme found in all tissues in the human body but is mostly concentrated in the bones, kidneys, liver, intestines, and placenta. It exists in different forms, depending on where it originates [1].
Its major function is to protect your intestinal tract against bacteria, aid in digestion, breakdown fats and some B vitamins, and promote bone formation [1].
High levels of ALP in the blood may indicate bone, liver, or bile duct disease.
ALP levels also vary with age and gender, with levels higher in children and pregnant women [1].
Higher ALP levels can occur in people with blood group B or blood group O [2].
In balance, ALP supports good health. In excess or deficiency, this enzyme can lead to a broad range of diseases [3].
When the liver is not functioning properly, ALP is released into the bloodstream. Additionally, any condition that affects bone growth or causes the increased activity of bone cells can increase ALP levels in the blood. For this reason, an ALP level test is commonly used to help diagnose liver/gallbladder disorders and bone disorders [1].
Note: Lab results are commonly shown as a set of values known as a “reference range”, which is sometimes referred to as a “normal range”. A reference range includes the upper and lower limits of a lab test based on a group of otherwise healthy people.
Your healthcare provider will compare your lab test results with reference values to see if your chloride results fall outside the range of expected values. By doing so, you and your healthcare provider can gain clues to help identify possible conditions or diseases.
Remember that some lab-to-lab variability occurs due to differences in equipment, techniques, and chemicals used. Don’t panic if your result is slightly out of range – as long as it’s in the normal range based on the laboratory that did the testing, your value is normal.
However, it’s important to remember that a normal test doesn’t mean a particular medical condition is absent. Your doctor will interpret your results in conjunction with your medical history and other test results.
And remember that a single test isn’t enough to make a diagnosis. Your doctor will interpret this test, taking into account your medical history and other tests. A result that is slightly low/high may not be of medical significance, as this test often varies from day to day and from person to person.
Symptoms of High Alkaline Phosphatase
The symptoms we discuss here are commonly associated with high alkaline phosphatase levels, but are not enough for a diagnosis. Work with your doctor to discover what underlying condition might be causing high alkaline phosphatase levels and to develop an appropriate plan to improve your health.
When caused by liver disease, symptoms of high ALP include [4, 5]:
- Itching
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Jaundice
- Swelling and pain in your stomach
- Dark-colored urine and/or light-colored stool
Symptoms caused by bone disorders include [6]:
- Bone or joint pain
- Enlarged or abnormally shaped bones
- Higher frequency of bone fractures
Causes of High Alkaline Phosphatase
While alkaline phosphatase may not necessarily cause harm to the body itself, elevated levels are associated with cancer, bone, liver, and kidney diseases [7].
Additionally, lifestyle factors, medication, and certain supplements can raise alkaline phosphatase levels. Work with your doctor to find out what causes your high alkaline phosphatase levels.
1) Birth control pills
Birth control pills can increase alkaline phosphatase to many times the level of a normal range [8].
2) Exercise
Exercise increases bone alkaline phosphatase levels after thirty and fifty minutes of moderate to intensive exercise in male cyclists, but it quickly returns to normal [9].
3) Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones stimulate alkaline phosphatase [10, 11]. Increased alkaline phosphatase levels are also correlated with hyperthyroidism [12].
4-5) Efavirenz and Cissus quadrangularis
Efavirenz, an anti-HIV drug, is associated with increased alkaline phosphatase levels in HIV patients. The high enzyme levels also associated with increased bone turnover and Vitamin D deficiency [13].
Cissus quadrangularis, a type of plant from the grape family, significantly increases alkaline phosphatase activity in cell culture. It also increases bone mineralization, which is likely due to the increased enzyme function [14].
6) Estrogen and Testosterone Metabolites
Estrogen, 5 alpha-DHT, and dehydroepiandrosterone (different types of hormones) can increase the enzyme’s activity (not the level in the blood) in human endometrial cancer cell lines [15].
Estrogen is also able to regulate the growth and expression of this enzyme in human bone marrow cell culture [16].
7) Biliary Obstruction and Liver Cancer
High liver alkaline phosphatase levels are associated with bile duct obstruction and liver cancer. The presence of liver alkaline phosphatase in patients may indicate the presence of a tumor in the bile duct [17].
8) Colon Cancer
Alkaline phosphatase levels are frequently high in patients with metastatic colon cancer. Increasing alkaline phosphatase levels are correlated with an increased cancer stage and may indicate that cancer has spread to the liver [18].
9) Breast Cancer
Women with breast cancer had elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase compared to normal healthy women. The increase of enzyme activities also indicates that the cancer is metastatic and spread to either the bone or liver [19, 20].
10) Leukemia
Leukemia patients, especially untreated ones, have high alkaline phosphatase levels. The placenta alkaline phosphatase level is a useful biomarker to help diagnose and treat leukemia [21].
11) Alzheimer’s
Alzheimer’s patients have higher tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase levels compared to healthy patients. The higher the alkaline phosphatase activity, the lower the brain function [22].
12) Paget’s Disease
Paget’s disease is a common disorder that affects bone strength and formation. Abnormally high levels of bone alkaline phosphatase can be an indicator of bone turnover, so while the enzyme does not cause the disease, it can be a helpful indicator [23].
13) Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is usually accompanied by elevated levels of total alkaline phosphatase in the blood. However, it is not the best indicator of vitamin D deficiency [24].
14) Heart Disease
Elevated alkaline phosphatase levels are associated with a higher risk of heart disease.
In a prospective study of more than 3,000 elderly men, the higher alkaline phosphatase levels predict higher risks of heart attacks, strokes, and increase mortality [25].
15) Liver Problems Associated with Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the gut lining upon gluten consumption. In cases of uncontrolled celiac disease where the patients continue to consume gluten, other liver and biliary tract disorders can occur. Elevated alkaline phosphatase levels are associated with these two disorders [26].
16) Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia is associated with high levels of alkaline phosphatase. The higher alkaline phosphatase levels correlate with worsened bone and other tissue damage in sickle cell anemia patients [27, 28].
In patients with sickle cell disease, higher levels of alkaline phosphatase are associated with vaso-occlusive crises involving the bones [28].
17) Epilepsy
Epileptic children have higher alkaline phosphatase levels compared to children without the disorder [29].
18) Genetic Factors
Different genes encode human alkaline phosphatases, i.e. [1]:
- ALPP for the alkaline phosphatase in the placenta
- ALPL (also called TNAP for Tissue Non-Specific Alkaline Phosphatase) for the alkaline phosphatase in the liver, bone, and kidney
Go to SelfDecode to learn how your genes can influence your alkaline phosphatase levels.
SelfDecode is a sister company of SelfHacked. The proceeds from your purchase of this product are reinvested into our research and development, in order to serve you better. Thanks for your support!
How to Reduce Alkaline Phosphatase
If your phosphatase alkaline levels are too high, discuss with your doctor what underlying health conditions are causing them and what strategies may help you lower them. Never implement them in place of what your doctor recommends or prescribes.
1) Support Your Liver
If your alkaline phosphatase levels are high because you have liver damage, you may look into natural ways to support the health of your liver. Your liver has the capacity to regenerate. Talk to your doctor about how to improve your liver health and read our 6-step protocol for liver regeneration. In a nutshell, you should take targeted liver-protective herbs and nutrients while adapting your diet and reducing alcohol intake.
Consider liver-protective supplements like:
- Milk thistle
- NAC (300mg if you are also taking milk thistle)
- Taurine (500 mg)
- Vitamin C (500 mg)
- B vitamins (low dosages)
- ALCAR and Lipoic acid
Vegetables like broccoli [30], onions [31], dandelion greens, cabbage, cauliflower and Brussels sprouts [32] also have a cleansing effect on the liver.
Here is a list of all foods and supplements that are good for your liver.
2) Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids reduce the levels of intestinal alkaline phosphatase, whereas omega-6 fatty acid increases the level of intestinal alkaline phosphatase in the gut [33].
3) Stop Smoking
Stop smoking, as it can increase ALP levels [34].
4) Coffee
Coffee intake is linked to lower ALP levels. Remember to stick to a moderate consumption to avoid unwanted effects such as high blood pressure and sleep disturbances [35].
5) Cinacalcet
Cinacalcet, a drug for chronic kidney disease, can reduce blood alkaline phosphatase levels by more than twenty percent in patients after 26 weeks of administration. This drug should be prescribed by a doctor and taken as recommended [36].
6) Resistance Exercise
In untrained male subjects, one single bout of resistance exercise can cause bone ALP activity to significantly decrease two and three days after the exercise [37].
7) Sun Exposure/Vitamin D
Since vitamin D deficiency has been linked with high alkaline phosphatase, be sure to check your levels. If you are deficient, get more sun and/or take vitamin D supplements. Reasonable sun exposure is a better way to increase your vitamin D levels than supplements.
Takeaway
Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme that helps you digest food and maintain strong bones. It’s concentrated in the liver, kidneys, gut, and bones. High levels may point to problems with these organs. Alkaline phosphatase is high if the blood levels surpass 130 U/L. High alkaline phosphatase doesn’t cause any symptoms directly. The symptoms will depend on your underlying health issue–such as liver or bone disorders. If your levels are high due to liver disease, you may want to take supplements and nutrients that will help your liver regenerate. Some good options include milk thistle, NAC, taurine, B vitamins, and vitamin C. Additionally, get enough sun, exercise, omega-3 fatty acids, and coffee. Reduce alcohol and stop smoking — they both lower alkaline phosphatase levels and support good health. Always talk to your doctor about any lifestyle and dietary interventions that you plan to implement.


